Virtualization in server infrastructure refers to the practice of creating virtual instances of computing resources, such as operating systems, applications, storage, and network resources, on a physical server. This allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical server, each operating independently of the others.
Virtualization has several advantages in server infrastructure, including increased flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. By creating multiple virtual instances on a single physical server, organizations can reduce their hardware and energy costs, while also making it easier to provision and manage resources.
There are several different types of virtualization technologies available for server infrastructure, including hypervisor-based virtualization, container-based virtualization, and virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI). Each of these technologies has its own benefits and drawbacks, depending on the specific needs of the organization.
virtualization has become an essential component of modern server infrastructure, providing organizations with the ability to optimize their resources, streamline their operations, and improve their overall IT efficiency.
Types of Virtualization:
There are different types of virtualization available for server infrastructure. Here are the three main types of virtualization:
Hypervisor-based Virtualization:
Also known as “full virtualization,” this type of virtualization is based on a layer of software called a hypervisor. The hypervisor enables multiple VMs to share a single physical server while maintaining their own isolated operating system, applications, and resources. The hypervisor manages the virtualized environment, providing access to physical resources such as CPU, memory, and storage.
Hypervisor-based virtualization offers a high level of isolation and security, as each VM runs in its own isolated environment. This type of virtualization is commonly used for server consolidation, where multiple physical servers are replaced by a single server running multiple VMs.
Container-based Virtualization:
This form of virtualization permits a couple of packages to run on a unmarried working system, with every software walking in its very own container. Containers are lightweight, portable, and provide a high level of resource utilization. They are created from images that contain all the necessary dependencies and configurations required for an application to run.
Container-based virtualization offers a high degree of agility and scalability, making it popular for cloud-native applications and microservices architectures. Container-based virtualization is less resource-intensive than hypervisor-based virtualization, making it ideal for running multiple applications on a single server.
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI):
This type of virtualization involves hosting desktop operating systems and applications on a centralized server and delivering them to end-users over a network. The end-users access the virtual desktops and applications from thin client devices or remote desktop protocols.
VDI allows organizations to centralize desktop management and provide employees with remote access to their desktops and applications from anywhere. This type of virtualization is often used in environments where employees require access to their desktops and applications from multiple locations or devices, such as in remote work scenarios.
Benefits of Virtualization:
1.Virtualization in server infrastructure offers several benefits, including:
Increased Efficiency: Virtualization enables organizations to run multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server, maximizing the use of hardware resources. This leads to improved efficiency, reduced hardware costs, and lower energy consumption. Virtualization also makes it easier to provision and manage resources, improving overall IT efficiency.
Enhanced Flexibility and Scalability:
Virtualization enables IT teams to quickly create, configure, and deploy new VMs, allowing them to respond quickly to changing business needs. With virtualization, organizations can easily scale resources up or down as needed, without the need for additional physical servers.
Improved Disaster Recovery:
Virtualization allows organizations to create backup and recovery solutions that are more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective than traditional physical server-based solutions. With virtualization, organizations can easily create and manage virtual machine images, which can be quickly restored in the event of a disaster.
Simplified Testing and Development:
Virtualization enables organizations to create isolated test environments that replicate production environments, allowing developers to test applications without impacting production systems. This reduces the risk of downtime and errors caused by untested applications.
Better Resource Utilization:
Virtualization enables IT teams to consolidate multiple physical servers into a single physical server running multiple VMs. This leads to better resource utilization, reducing the need for additional hardware and lowering energy consumption.
Increased Security:
Virtualization can improve security by providing greater isolation between VMs. Each VM runs in its own isolated environment, reducing the risk of malware and other security threats spreading across the server. Virtualization also makes it easier to implement security policies across multiple VMs.
virtualization offers numerous benefits to organizations, including increased efficiency, flexibility, scalability, and security, while also reducing costs and simplifying resource management.
Virtualization vs. Physical Servers:
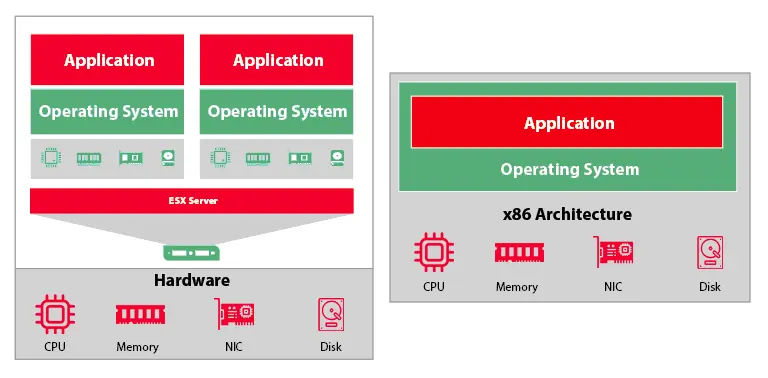
Virtualization and physical servers both have their own advantages and disadvantages. Here are some key differences between the two:
Hardware Utilization:
Virtualization allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical server, allowing for greater hardware utilization. Physical servers, on the other hand, typically run a single operating system and application, leading to lower hardware utilization.
Scalability:
Virtualization allows for greater scalability, as additional VMs can be easily created and deployed on existing hardware resources. Physical servers require the purchase of new hardware to scale.
Maintenance:
Virtualization simplifies maintenance tasks such as software upgrades, patch management, and cloud backup solutions, as they can be performed on a single physical server hosting multiple VMs. Physical servers require maintenance tasks to be performed on each individual server.
Cost:
Virtualization can lead to cost savings by reducing the number of physical servers required and the associated hardware, energy, and maintenance costs. However, virtualization also requires additional software and management tools, which can increase costs
Performance:
Virtualization may introduce some performance overhead due to the additional layer of software (the hypervisor) that manages the virtualized environment. Physical servers offer more direct access to hardware resources, which can lead to higher performance.
Security:
Virtualization can improve security by providing greater isolation between VMs. However, a single compromised host machine can potentially impact multiple VMs. Physical servers offer more physical security as they can be physically secured and locked away.
virtualization offers greater hardware utilization, scalability, and simplified maintenance, while physical servers offer more direct access to hardware resources and potentially better performance and physical security. Organizations need to evaluate their specific needs and requirements when deciding between virtualization and physical servers.
Virtualization and Cloud Computing:

Virtualization and cloud computing are closely related concepts, but they are not the same thing. Here are some key differences between virtualization and cloud computing:
| Aspect |
Virtualization |
Cloud Computing |
| Scope |
Abstraction of hardware |
Delivery of computing services |
| Management |
Virtual machines and hardware |
Entire stack of computing services |
| Deployment |
On-premises or private cloud |
Public, private, or hybrid cloud |
| Service Model |
Infrastructure technology |
IaaS, PaaS, SaaS |
| Cost |
Potential cost savings |
Pay-as-you-go model |
| Scalability |
Multiple VMs on existing HW |
Access to dynamic pool of resources |
Virtualization and Disaster Recovery:

Virtualization can be an essential tool for disaster recovery (DR) planning and implementation. Here are some ways virtualization can help with disaster recovery:
Improved Recovery Time Objective (RTO):
Virtualization can help improve RTO, which is the time it takes to restore a system after a disaster. By virtualizing servers, the entire server environment can be captured as a single image or snapshot, making it easier and faster to restore.
Increased Availability:
Virtualization can improve availability by allowing for the easy migration of virtual machines (VMs) between physical hosts. If a physical host fails, the VMs can be quickly moved to another host, minimizing downtime.
Simplified Backup and Restore:
Virtualization simplifies the backup and restore process by providing a single point of control for multiple VMs. Virtualization also enables efficient use of storage resources through features such as thin provisioning and deduplication.
Testing and Validation:
Virtualization provides an ideal environment for testing and validating disaster recovery plans. By creating a duplicate environment in a virtual environment, organizations can test and validate DR plans without impacting production systems.
Cost Savings:
Virtualization can lead to cost savings by reducing the need for physical servers and hardware, as well as simplifying the backup and restore process.
virtualization can improve disaster recovery planning and implementation by improving RTO, increasing availability, simplifying backup and restore, providing a testing and validation environment, and reducing costs. By leveraging the benefits of virtualization, organizations can create a more resilient and reliable disaster recovery strategy.
Virtualization Security:
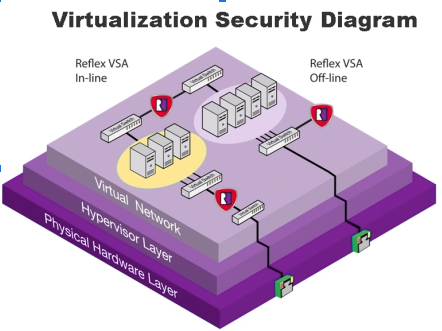
Virtualization security refers to the measures taken to secure the virtualized infrastructure, including virtual machines (VMs), virtual networks, and virtual storage. Here are some key aspects of virtualization security:
Hypervisor Security:
The hypervisor is the core component of virtualization technology that enables the creation and management of VMs. Hypervisor security involves securing the hypervisor itself against potential attacks, such as unauthorized access, malware, and denial-of-service attacks.
Network Security:
Virtualization networks can be vulnerable to the same types of attacks as physical networks, such as hacking, malware, and phishing attacks. Network security measures for virtualization include network segmentation, virtual firewalls, and intrusion detection and prevention systems.
Storage Security:
Virtualization storage can also be vulnerable to attacks, such as data theft and data tampering. Storage security measures for virtualization include encryption, access controls, and backup and recovery procedures.
VM Security:
Virtual machines are vulnerable to the same types of attacks as physical machines, such as viruses, malware, and hacking attempts. VM security measures include regular software patching, antivirus and anti-malware software, and secure configurations.
Administrative Security:
Administrative security involves securing the management interfaces used to control the virtualized environment, such as management consoles, APIs, and command-line interfaces. Administrative security measures include access controls, strong authentication mechanisms, and audit logging.
Compliance and Governance:
Virtualized environments must adhere to the same compliance and governance requirements as physical environments. This includes maintaining compliance with regulations such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR, and ensuring proper governance of the virtualized infrastructure.
virtualization security involves securing the hypervisor, networks, storage, virtual machines, administrative interfaces, and compliance and governance requirements. By implementing proper security measures, organizations can reduce the risks associated with virtualization and maintain a secure virtualized infrastructure.
How HostingRaja’s 24/7 Managed Support helps you?
Providing 24/7 support for a Virtualization-Server involves ensuring that the database system remains available and operational at all times. Here are six key points to consider when providing support for a Virtualization-Server
Monitoring: Monitoring the health and performance of the servers is essential for identifying and resolving issues before they affect the system. Tools such as Virtualization-Server Cloud Manager or Ops Manager can provide real-time monitoring and alerting for the servers.
Automation: Automating routine tasks, such as backups, updates, and failover, can help reduce the risk of human error and ensure that the system is always running optimally. Tools such as Ansible or Puppet can be used to automate these tasks.
Security: Ensuring that the Virtualization-Server is secure is critical for protecting sensitive data. This involves implementing appropriate security measures, such as firewalls, access controls, and encryption, and regularly reviewing and updating security policies.
Disaster Recovery: Having a disaster recovery plan in place can help minimize downtime and data loss in the event of a catastrophic failure. This involves regularly backing up data and having a plan in place for restoring the database in the event of a failure.
Response Time: When issues do occur, it’s essential to respond quickly to minimize the impact on the system. Having a dedicated support team available 24/7 to handle issues as they arise is critical for ensuring that the system remains operational.
Continuous Improvement: Finally, continuously improving the Virtualization-Server over time can help optimize its performance and ensure that it remains scalable and resilient. This involves regularly reviewing system metrics and performance data, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing changes to optimize the system.
Cost Savings: Hiring a full-time in-house DBA can be costly. HostingRaja database administration service can help reduce costs by only paying for the services needed, rather than having a full-time employee on payroll with benefits.
Access to Expertise: Database administration is a highly specialized field. Our 10+ years of experts can provide access to a broad range of skills and experience that may not be available in-house. This can help improve the overall performance, efficiency, and reliability of the database system.
Flexibility and Scalability: Our 24/7 Managed support gives you flexibility and scalability. As business needs change, you can easily adjust the level of service provided, adding or removing resources as needed.
Reduced Risk: HostingRaja team of experts can help reduce the risk of data breaches or other security concerns. External providers have a dedicated focus on security and can provide additional resources, such as data backups and disaster recovery plans.
24/7 Support: Our 24/7 managed support team can offer around-the-clock support, ensuring that any issues are promptly addressed, even outside of business hours.
Access to New Technologies: Our team often has access to the latest technologies and software updates. Outsourcing can provide access to new tools and features, ensuring that the database system remains up-to-date and optimized.
Improved Performance: HostingRaja database administration can help improve overall performance by ensuring that the database is properly optimized and configured for maximum efficiency.
Overall, HostingRaja’s database administration can provide cost savings, access to expertise, flexibility, reduced risk, 24/7 support, improved focus, access to new technologies, and improved performance.