Domain Vs Hosting: Definition And Difference
Table of Contents
- 1 Domain Vs Hosting: Definition And Difference
- 2 Domain Name vs Web Hosting
- 3 Domain Names and Domain Registration
- 4 Buy Cheap Domain Names (from Rs.99)
- 5 Steps in Domain Registration
- 6 Structure of a Domain Name
- 7 Types of Domains
- 8 Why Domain Registration Matters:
- 9 How Domain and Hosting Work Together
- 10 User Types Your Domain
- 11 Browser Sends a DNS Request
- 12 Server Receives Request
- 13 Browser Renders the Website
Introduction
Domain names and web hosting are two essential elements that are frequently mentioned while building a website. Although they collaborate to make webpages accessible, they have distinct functions.
One essential component of the internet that makes it easier for consumers to access websites is a domain name. Although we frequently consider domain names to be the addresses we enter into the search bar of our browser, much more is happening in the background. By translating into the intricate technical addresses that computers use to interact with one another, a domain name acts as an easily navigable identification.
An IP (Internet Protocol) address that is readable by humans is called a domain name. Each internet-connected device has an IP address, which is a string of numbers such as 192.168.1.1. This string serves as the internet’s unique identification for a website. However, domain names are utilised as a more readable and memorable alternative to IP addresses because IP addresses are hard for people to remember.
For instance, to access Google, type google.com rather than 173.194.223.113. By serving as a shortcut for these IP addresses, domain names improve internet accessibility and usability.
Domain Name vs Web Hosting
| Feature | Domain Name | Web Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| Description | A domain name is the online address that visitors enter into a browser to access your website. | Web hosting is where your website’s files (HTML, photos, and videos) are stored. |
| Function | Functions as a digital address, directing visitors to your site. | Makes your website available to users via the internet by storing your website files. |
| Key Features |
|
|
| Example Providers | GoDaddy, Namecheap, Google Domains | HostingRaja, Bluehost, SiteGround |
- Top-Level Domain (TLD): This is the extension found at the end of the domain name, such as .com, .org, or .net.
- Second-Level Domain (SLD): This is the unique name chosen by the owner, like google in google.com.
- Together, these elements form a complete domain name, directing users to the correct IP address
- Domain Name Lookup: Your browser sends a request to a DNS resolver, a server made specifically to convert domain names into IP addresses, when you type a domain name (for instance, example.com) into the browser.
- Query for DNS: The DNS resolver looks for the domain’s IP address in its local cache. If not, it queries the root server and then other DNS servers. The location of Top-Level Domain (TLD) like .com or .org information is known to this service.
- TLD Name Server: A TLD name server, which holds data on domains under a particular TLD, receives the request from the root server. After that, the TLD server sends the request to the authoritative name server, which is in possession of the domain name’s IP address.
- IP Address Return: The DNS resolver receives the correct IP address from the authoritative name server. The browser then receives this IP address.
- Website Loading: After obtaining the IP address, the browser makes a request to the web server that houses the files on the website, and the loading process starts. After obtaining the IP address, the browser makes a request to the web server that houses the files on the website, and the loading process starts.
A domain name must be registered with a domain registrar in order to be used. The rights to use a certain domain name for a predetermined amount of time, usually a year or more, are purchased when someone registers a domain. After registration is finished, the DNS links the domain to a particular IP address.
Well-known domain registrars provide simple tools for managing, renewing, and registering domain names. You can hold the right to use a domain name, but in order to keep ownership, you will need to renew your registration on a regular basis.
Domain names are critical to the functioning of the internet. They simplify navigation for users and contribute to branding and online presence. Businesses and individuals rely on memorable domain names to enhance user experience and improve search engine visibility. A well-chosen domain name can increase website traffic and credibility.
Domain Names and Domain Registration
In order to create an online presence, a domain name is necessary. It serves as a memorable and user-friendly representation of your brand or company, acting as a digital address that guides consumers to your website. Users would have to memorise complex numerical IP addresses in order to access a website in the absence of a domain name. Rather than entering “216.58.217.206” to access Google’s homepage, individuals can instead type “google.com.”
A domain name is the unique string of text that identifies a website. Every website needs one to be accessible on the internet. Domain names consist of two main parts:
- Top-Level Domain (TLD): This is the extension that follows the domain name, such as .com, .org, .net, or country-specific codes like .in (India) or .uk (United Kingdom).
- Second-Level Domain (SLD): This is the main part of the domain name, like “google” in “google.com” or “wikipedia” in “wikipedia.org.” The SLD usually reflects the name of the brand or business.
Together, these components make up a domain name like “example.com” or “business.net.”
The importance of a domain name cannot be overstated in the digital world:
- Brand Identity: A domain name is crucial for branding. It helps establish an online identity that is easy to recognize and recall.
- Trust and Professionalism: A domain that aligns with your brand name, especially with a familiar TLD like “.com,” enhances credibility and trustworthiness.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Although not the primary factor, a well-chosen domain name can improve your website’s visibility on search engines, making it easier for users to find you online.
Domain registration is the process of reserving a domain name on the internet for a specific period, typically one year or more. To register a domain name, you need to go through a domain registrar—an organization that manages the reservation of internet domain names. Some popular domain registrars include:
- Spidyhost
- tmdhosting
- Bluehost
- webhostpython
When you register a domain name, you own the exclusive right to use it for your website, emails, or other online platforms.
Steps in Domain Registration
- Choosing a Domain Name: Start by brainstorming domain names that reflect your business, brand, or personal project. Ensure that the name is easy to spell, memorable, and available.
- Checking Domain Availability: Use a domain registrar or domain search tool to see if the domain name you want is available. If it’s already taken, many registrars will suggest alternative TLDs or slight variations of the name.
- Selecting a Domain Registrar: Once you find an available domain name, choose a reliable registrar to complete the registration. Compare prices, customer support, and added features like privacy protection or email forwarding.
- Registering the Domain: After selecting your domain, you’ll need to provide your contact information and pay a registration fee. Typically, domain names are registered for one year, but you can opt to extend the duration.
- Pointing the Domain to a Web Host: Once your domain name is registered, you can point it to your website’s server by adjusting the DNS (Domain Name System) settings. This ensures that visitors who type in your domain will be directed to your website.
Domain names come with various extensions or TLDs. Here are some common categories:
- Generic TLDs (gTLDs): Extensions like .com, .net, and .org are the most popular and widely recognized.
- Country Code TLDs (ccTLDs): These are location-specific extensions, such as .us (United States), .uk (United Kingdom), or .ca (Canada).
- New gTLDs: In recent years, newer domain extensions like .shop, .online, and .blog have been introduced, offering more options for branding.
Once registered, it’s essential to protect your domain name. Many registrars offer domain privacy protection, which hides your personal information (such as name and contact details) from being publicly displayed in the WHOIS database, a global database of registered domain names.
You should also monitor your domain’s expiration date. If you don’t renew your domain registration on time, it could be purchased by someone else, leading to a loss of ownership.
Structure of a Domain Name
A domain name is typically structured in three parts:
- Subdomain: Often “www” (though optional).
- Second-level domain (SLD): The main part of the domain, like “example” in “example.com.”
- Top-level domain (TLD): The extension, such as “.com,” “.org,” or “.net.”
For example, in www.example.com:
- www is the subdomain.
- example is the second-level domain.
- .com is the top-level domain (TLD).
Types of Domains
Finding the ideal extension can be facilitated by being aware of all your alternatives if you wish to register a domain name. Here are the main types of domain names:
- Generic Top-Level Domains (gTLDs): Extensions like “.com”, “.org”, and “.net”.
- Country Code Top-Level Domains (ccTLDs): Domain extensions that are specific to countries, such as “.in” for India or “.uk” for the United Kingdom.
- New gTLDs: Custom domains like “.tech”, “.shop”, or “.blog”.
| TLD | Registration | Renewal | Transfer |
|---|---|---|---|
| .com | ₹950.00 | ₹1050.00 | ₹1050.00 |
| .co.uk | ₹670.00 | ₹670.00 | ₹670.00 |
| .info | ₹1564.00 | ₹1564.00 | ₹1564.00 |
| .net | ₹1260.00 | ₹1260.00 | ₹1260.00 |
| .xyz | ₹1999.00 | ₹1999.00 | ₹1999.00 |
Once you’ve found an acceptable alternative, register it. To register a domain name with Hostingraja, click the Add to Cart button next to your desired domain name.

Why Domain Registration Matters:
- Brand Identity: A well-chosen domain name can strengthen your brand and improve recognition.
- Credibility: Having your own domain (instead of using a free subdomain) adds professionalism and trustworthiness to your website.
- SEO Benefits: An appropriate domain name can help with search engine optimization (SEO), making it easier for users to find your site through search engines.
Domain Privacy:
When registering a domain, your personal contact details (such as name, address, and email) are listed in the public WHOIS directory. Many registrars offer domain privacy protection, which replaces your personal information with generic contact details to protect your privacy.
Web hosting refers to a service that allows individuals or organizations to store their website files (such as HTML, images, and other multimedia content) on a server that is accessible via the internet. This server is provided by a web hosting company, which offers the technology and infrastructure needed to ensure that a website is available online 24/7.
When someone types your website’s domain name (like www.Hostingraja.com) into their browser, their computer connects to the web server where your site is hosted, retrieving the files necessary to display the website.
- Shared Hosting: Shared Hosting is a popular and inexpensive web hosting solution in which numerous websites share a single server’s resources. This sort of hosting is perfect for small enterprises, startups, and personal websites because it is inexpensive and simple. Shared hosting prices range from ₹85.00 to ₹184.00 per month.
- VPS hosting: A physical server is virtually partitioned, providing users with a private environment and dedicated resources. This hosting type is ideal for websites with medium-to-high traffic. VPS hosting rates range from ₹549.00 to ₹1699.00 per month.
- Web Hosting: Web hosting costs between ₹59.00 and ₹184.00 a month and allows multiple websites to share a single physical server with limited storage and resources. Shared hosting is the most cheap option available and is ideal for small businesses or personal websites.
- WordPress hosting: It offers an optimised environment, performance, and security for hosting WordPress websites. This hosting package includes WordPress-specific functionality and customisation choices, allowing you to simply manage and build your website. WordPress managed hosting options range from ₹99.00 to ₹149.00 per month.
- Disk Space: Storage for your website’s files and data.
- Bandwidth: The amount of data transfer allowed between your website and its visitors.
- Control Panel: A user-friendly interface for managing your website and server settings.
- Security: Features like SSL certificates, firewalls, and regular backups to protect your data.
Choosing the right web hosting depends on the size, traffic, and complexity of your website. For example, shared hosting is cost-effective for smaller websites, while larger websites with high traffic may benefit from dedicated or cloud hosting.
A domain name and web hosting work together to create a website by serving two distinct roles in making your site accessible on the internet.
Domain Name: This is the address of your website (e.g., www.Hostingraja.com) that people type into their web browsers to access your site. It’s like the digital address for your business or blog, helping visitors locate your website. You purchase and register a domain name through a domain registrar.
Web Hosting: This is the physical space where your website’s files, such as HTML, images, and videos, are stored. When a user enters your domain name, the web hosting server delivers the stored files to their browser, allowing the website to be displayed.
How Domain and Hosting Work Together
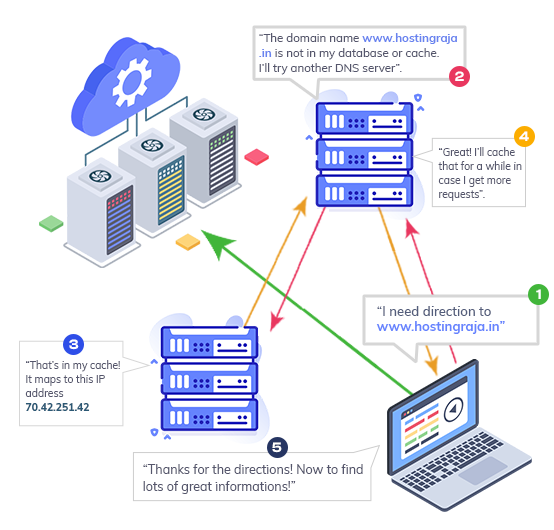
User Types Your Domain
A user types your domain name into their browser.
Browser Sends a DNS Request
The browser sends a request to the DNS (Domain Name System), which looks up the IP address of the server hosting your website.
Server Receives Request
The server (provided by your web host) receives the request and sends the website files to the browser.
Browser Renders the Website
The browser renders the files, and the user can now view the website.
Essentially, the domain name acts as the “address” of your website, while web hosting is the “home” where all the website’s content is stored and managed. Together, they enable visitors to easily find and view your website.
-

KINGSTON AJITH
Senior Content Writer @ HostingRajaA seasoned Senior Content Writer with over 5 years of experience in the tech industry, specializing in web hosting. Passionate about creating unique, high-quality content for articles, blogs, and web pages. As a dedicated learner, continually improving writing skills and overseeing all online content and communications to ensure quality and consistency.
